Active IRS versus Passive IRS
Wireless Communication Aided by Intelligent Reflecting Surface: Active or Passive?. Changsheng You et.al. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, Dec. 2021 (pdf) (Citations 9)
Quick Overview
a single antenna access point communicates with a single-antenna user
rate-maximization with passive/active IRS:
- active IRS should be deployed closer to the RECEIVER with the decreasing amplification power of the active IRS (known in Lemma1)
- passive IRS is known to be near the transmitter or receiver to minimize the path-loss (known in my-note section 3.2)
optimal the placement:
- passive IRS outperform active IRS when the number of element is sufficiently large/ the amplification power of the active IRS is too small.(known in my-note section 3.3)
- optimal placement to maximize the weighted sum-rate of uplink and downlink communications. Passive is more likely to achieve superior rate performance.(known in my-note section 3.4)
Model
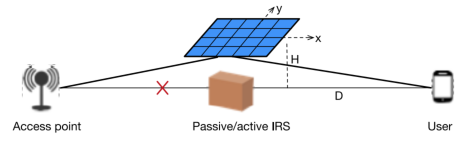
Main Work
Active IRS
\[ y_{\mathrm{act}}=\boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{IU}}^{H} \eta \boldsymbol{\Theta}\left(\boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{AI}} s+\boldsymbol{n}_{\mathrm{F}}\right)+n \]
achievable rate = \(\log_2(1+\text{SNR})=\log _{2}\left(1+\frac{P_{\mathrm{A}}\left|\boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{IU}}^{H} \eta \boldsymbol{\Theta} \boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{AI}}\right|^{2}}{\left\|\boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{IU}}^{H} \eta \boldsymbol{\Theta}\right\|^{2} \sigma_{\mathrm{F}}^{2}+\sigma^{2}}\right)\)

得到优化目标(P1):

然后由于(4a)恒成立(是e的指数次项),且(4e)等价形式\(P_{\mathrm{F}} \geq N P_{\mathrm{A}} \beta /\left(D^{2}/4+H^{2}\right)+N \sigma_{\mathrm{F}}^{2}\)
(原文这个等式有错误,$D^2$没有乘系数1/4)得到等效的(P2):

因为信道建模为: \[ \boldsymbol{h}_{\mathrm{AI}}=h_{\mathrm{AI}} \boldsymbol{a}_{\mathrm{r}}\left(\theta_{\mathrm{AI}}^{\mathrm{r}}, \vartheta_{\mathrm{AI}}^{\mathrm{r}}, N\right), \text { where } h_{\mathrm{AI}} \triangleq \sqrt{\beta / d_{\mathrm{AI}}^{2}} e^{-j \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda} d_{\mathrm{AI}}} \] 优化目标就是max(SINR)
整理得到优化目标(P3):

可以得到Lemma1:AP-IRS的距离\(x_{AI}\)随\(P_F\)的增大而单调递减;随\(N\)非减。(随\(P_F\)的单调递减证明没看懂)
然后有给定的lemma2:
给定\(H\ll D\): \[ \max \left\{C_{1} d_{\mathrm{AI}}^{2}, C_{2} d_{\mathrm{IU}}^{2}\right\} \gg C_{3} d_{\mathrm{AI}}^{2} d_{\mathrm{IU}}^{2}, \forall x_{\mathrm{AI}} \in[0, D] \] 如果有: \[ \sqrt{P_{A} \beta} / \sigma_{\mathrm{F}}+\sqrt{P_{F} \beta} / \sigma \gg D \]
所以由Lemma2可以得到优化目标(P4):

这就是个高中数学题:

Passive IRS
与active IRS 类似,得到\(\mathrm{SNR}_{\text {pas }}^{(\mathrm{DL})}=\frac{P_{\mathrm{A}} \beta^{2} N^{2}}{d_{\mathrm{AI}}^{2} d_{\mathrm{IU}}^{2} \sigma^{2}}\),然后由参考文献给出,对于Passive IRS,\(x_{AI}=0\quad or\quad D\),得到: \[ \mathrm{SNR}_{\text {pas }}^{(\mathrm{DL}) *} \approx \widetilde{\mathrm{SNR}}_{\text {pas }}^{(\mathrm{DL})} \triangleq \frac{P_{\mathrm{A}} \beta^{2} N^{2}}{H^{2}\left(D^{2}+H^{2}\right) \sigma^{2}} \]
Active IRS versus Passive IRS


即:
给定较小的\(H\),当Active IRS的功率\(P_F\)太小或者IRS装配了大量的elements(\(N\)很大),Passive IRS 往往优于 Active IRS。
Joint Downlink and Uplink communication
maximize the weighted sum-rate of uplink and downlink communications.
对于一个较小的\(P_F\),active IRS 在上行时应该接近AP, 在下行接近User(see Lemma1)。(需要权衡)
而Passive IRS,IRS放置于AP或者User,对于上行/下行都是最佳(因为上行的\(x_{AI}=0 orD\)和下行的最佳\(x_{AI}=Dor0\)是相同的)。(直接最佳)
Simulation
参数设置:
1 | |
Fig. 2
对比Optimal位置优化和Suboptimal位置优化,证明作者提出的Suboptimal是有效的:
首先是Optimal way,对应于(P3)

1 | |
然后是Suboptimal way,对应于(P4):
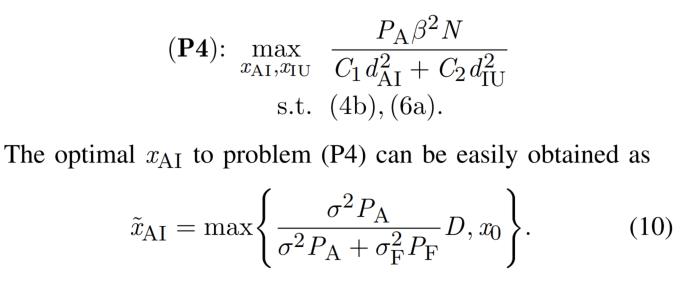
1 | |
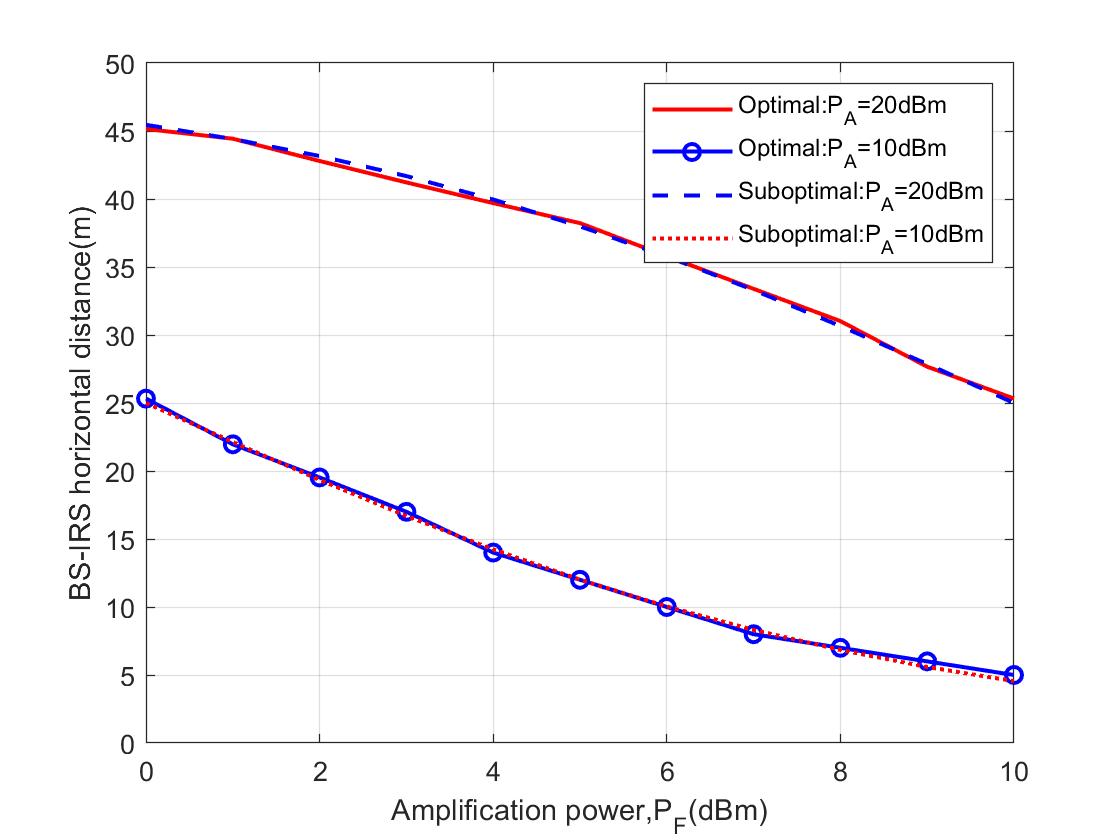
Fig. 3
Active IRS的achievable rate需要先算SNR,再由\(R=\log_2(1+\text{SNR})\)得到。为了方便计算,这里我用Suboptimal优化位置。对应于(eqn.11)

1 | |
Passive IRS同理:

1 | |

Fig. 4
计算weighted sum-rate,意味存在两个分配问题:
- IRS位置
- 上行、下行分配的时间(我是这么理解\(w^{(UL)}\)和\(w^{(DL)}\))
对于Active IRS,对应(P6):
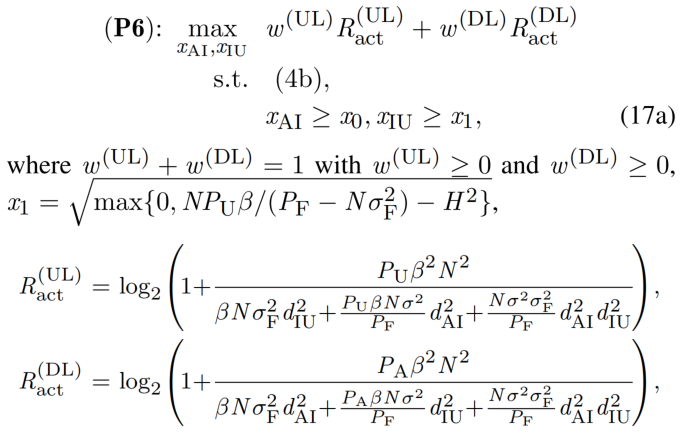
1 | |
对于Passive IRS,对应(P7):

1 | |

Fig. 5(结果和论文中有一定差异)
考虑\(H\)对weighted sum-rate 的影响,Active IRS:
1 | |
Passive IRS:
1 | |
